manganese into plants

The Role Of Manganese In Plants – How To Fix Manganese
May 17, 2021 Manganese is one of nine essential nutrients that plants require for growth Many processes are dependent on this nutrient, including chloroplast formation, photosynthesis, nitrogen metabolism, and synthesis of some enzymes This role of manganese in plants is extremely crucialManganese is an essential plant micronutrient It is absorbed by plants as Mn 2+ Manganese is an immobile nutrient and, therefore, deficiency symptoms show up on younger leaves first A manganese level of 20 to 40 ppm (mg kg –) in plant tissue is sufficient for most plantsManganese in plants and soil CropaiaMar 26, 2020 Manganese (Mn) is an important micronutrient for plant growth and development and sustains metabolic roles within different plant cell compartments The metal is an essential cofactor for the oxygenevolving complex (OEC) of the photosynthetic machinery, catalyzing the watersplitting reaction in photosystem II (PSII)Frontiers Manganese in Plants: From Acquisition to

THE FUNOTION AND DISTRIBUTION OF' MANGANESE IN
THE OCCURRENCE OF MANGANESE IN PLANTS The earliest record reporting the occurrence of manganese inplants is furnished us by Scheele,3 who pointed out that the ash of the seed of thewild anise contains a smallamount of manganese, while a con Riderably largerportionoccurs in Sep 11, 2021 Manganese becomes plant available after release of Mn2 into the soil solution Mn2 transport to the root surface by mass flow and diffusion followed by uptake into the root Manganese is one of nine essential nutrients that plants require for growthManganese In Plants Plants BYApr 12, 2021 Manganese is used in plants as a major contributor to various biological systems including photosynthesis, respiration, and nitrogen assimilation Manganese is also involved in pollen germination, pollen tube growth, root cell elongation and resistance to root pathogensRole of Manganese in Plant Culture PROMIX Greenhouse

How to Apply Manganese Sulfate to Plants Home Guides
Manganese is a micronutrient that is commonly deficient in soils with a pH level above 65 When your plants are lacking of this mineral, they exhibit visible symptoms For example, beans and manyManganese in soils is present in three oxidation states: Mn+2, Mn+3 and Mn+4 of which Mn+2 is the primary form in which Mn is absorbed by plants Manganese becomes plant available after release of Mn+2 into the soil solution, Mn+2 transport to the root surface by mass flow and diffusion, followed by uptake into the rootManganese Cornell UniversityManganese (Mn) functions primarily as part of enzyme systems in plants It activates several important metabolic reactions and plays a direct role in photosynthesis Micronutrient With Giant Benefits Manganese accelerates germination and maturity while increasing the availability of Manganese Crop Nutrients Mosaic Crop Nutrition

Manganese In Plants Plants BY
Sep 11, 2021 Manganese becomes plant available after release of Mn2 into the soil solution Mn2 transport to the root surface by mass flow and diffusion followed by uptake into the root Manganese is one of nine essential nutrients that plants require for growthManganese Manganese is a plant micronutrientIt fulfils a number of roles and is used in photosynthesis (manganese is important for a number of aspects of photosynthesis), synthesis of chlorophyll and nitrogen absorption as well as the synthesis of riboflavin, ascorbic acid and caroteneManganese in plants and soilManganese in soils is present in three oxidation states: Mn+2, Mn+3 and Mn+4 of which Mn+2 is the primary form in which Mn is absorbed by plants Manganese becomes plant available after release of Mn+2 into the soil solution, Mn+2 transport to the root surface by mass flow and diffusion, followed by uptake into the rootManganese Cornell University

Manganese in Crop Production Mosaic Crop Nutrition
Manganese (Mn) is an essential plant mineral nutrient, playing a key role in several physiological processes, particularly photosynthesis Manganese deficiency is a widespread problem, most often occurring in sandy soils, organic soils with a pH above 6 and heavily weathered, tropical soils It is typically worsened by cool and wet conditions (Alloway 2008)Mar 06, 2018 Deficiency symptom of manganese in plants The middle leaves develop interveinal small chlorotic patches and under continued deficiency the number increases resulting into chlorotic striping parallel to venation in cereals These chiorotic spots become necrotic and turn red, brown or reddish brown There are many physiological disorders termed Function And Deficiency Symptom Of Manganese In PlantsJul 10, 2019 Why Plants Often Struggle to Absorb Sufficient Quantities of Zinc, Manganese and Iron Soils in the Western United States are characteristically alkaline, meaning they have a pH greater than 70 These are conditions under which many of the essential mineral for plant growth can be tenaciously locked in the soil, unavailable for plant useThe Roles of Zinc, Manganese, and Iron in Plant Nutrition

Transport and detoxification of manganese and copper in plants
This manganese uptake activity was inhibited by cadmium, iron(II) and zinc, suggesting that IRT1 can transport these metals However, IRT1 did not complement a copper uptakedeficient yeast mutant (ctr1), implying that this transporter is not involved in the uptake of copper into plant Manganese can exist in 11 oxidation states, ranging from 3 to +7, but the most common ones are: +2 (eg, MnCl 2) and +4 (eg, MnO 2) 21 Manganese behaviour in the aquatic environment Natural waters, such as lakes, streams, rivers and oceans, contain variable quantities of dissolved manganese, ranging from 10 to 10,000 Íg l1 In water Manganese: A New Emerging Contaminant in the EnvironmentNov 26, 2017 Manganesedeficient beet leaf on left, normal leaf on right A first step might be a general feeding by scratching leaf mold into the soil Summer is a bit early for gathering leaf mold, but Restoring Soil Nutrients Organic Gardening MOTHER

The Effect of Excess Iron in Plants Home Guides SF Gate
Nov 24, 2020 When it comes to the effect of iron on plant growth, other nutrients come into play as well For example, iron and manganese both play an important role in plant Characteristics and occurrence Manganese (Mn) is frequently an abundant constituent of soils, but its low solubility at neutral and alkaline pH prevents excessive uptake by plants Therefore, manganese toxicity is nearly always associated with acid soilsWaterlogging may also induce or exacerbate manganese toxicity, as anaerobic conditions cause higher oxides of manganese to be reduced to Manganese toxicity LucidcentralThere are 7 essential plant nutrient elements defined as micronutrients [boron (B), zinc (Zn), manganese (Mn), iron (Fe), copper (Cu), molybdenum (Mo), chlorine (Cl)] They constitute in total less than 1% of the dry weight of most plants The following discussion focuses primarily on the soil characteristics for the micronutrients a Boron (B)3 Micronutrients

The Biochemical Properties of Manganese in Plants
Manganese (Mn) is an essential micronutrient with many functional roles in plant metabolism Manganese acts as an activator and cofactor of hundreds of metalloenzymes in plants Because of its ability to readily change oxidation state in biological systems, Mn plays and important role in a broad range of enzymecatalyzed reactions, including redox reactions, phosphorylation, decarboxylation Aug 10, 2018 Manganese is a micronutrient that is taken into the plant in extremely small quantities Manganese never occurs in nature as a pure element, it immediately combines with oxygen or other elements Manganese is actually one of the least understood AND Nutrient of the Month – Manganese Turf DietitianManganese (Mn) is an essential micronutrient with many functional roles in plant metabolism Manganese acts as an activator and cofactor of hundreds of metalloenzymes in plants Because of its ability to readily change oxidation state in biological systems, Mn plays and important role in a broad range of enzymecatalyzed reactions, including redox reactions, phosphorylation, decarboxylation The Biochemical Properties of Manganese in Plants

Manganese In Plants Plants BY
Sep 11, 2021 Manganese becomes plant available after release of Mn2 into the soil solution Mn2 transport to the root surface by mass flow and diffusion followed by uptake into the root Manganese is one of nine essential nutrients that plants require for growthManganese sulfate is readily available at most garden centers and works well for this Be sure to dilute any chemical nutrients to half strength to avoid nutrient burn Generally, application rates for landscape plants are 1/3 to 2/3 cup of manganese sulfate per 100 square feetHow do you add manganese to plants? AskingLotThis circular deals with the problem of manganese toxicity of plants in Florida Plants grown in artificial soilless media in containers and those grown in mineral soil can both experience toxicity from the uptake of excess amounts of manganese SYMPTOMS OF MANGANESE TOXICITY: Symptoms of manganese toxicity generally fall into two types TheMANGANESE TOXICITY OF PLANTS IN FLORIDA

Manganese matters: feeding manganese into the secretory
Jul 08, 2021 Manganese (Mn) is an essential element for plants, playing major roles as a cofactor of enzymes involved in photosynthesis and oxygen species detoxification (Schmidt Husted, 2019)Manganese acts in various plant cell compartments and needs to be transported in chloroplasts and mitochondria (He et al, 2021)The manganese/calcium (Mn/Ca) efflux transporters of the In soils, manganese is known to interact with a handful of other elements Most prominently, manganese is observed to interfere with the availability of cobalt to plants from soils via a strong affinity of manganese oxides to native cobalt Also, in acidic soils that contain a large amount of manganese, iron absorption by plants can be affectedEcological Soil Screening Levels for ManganeseMay 22, 2019 Manganese (Mn), an essential element for plants, can be toxic when present in excess Stylo (Stylosanthes) is a pioneer tropical legume with great potential for Mn tolerance, but its Mn tolerance mechanisms remain poorly understood In this study, variations in Mn tolerance were observed among nine stylo genotypes Stylo genotype ‘RY5’ exhibited the highest Mn tolerance compared to the Physiological responses and proteomic BMC Plant Biology

Manganese: A New Emerging Contaminant in the Environment
Manganese can exist in 11 oxidation states, ranging from 3 to +7, but the most common ones are: +2 (eg, MnCl 2) and +4 (eg, MnO 2) 21 Manganese behaviour in the aquatic environment Natural waters, such as lakes, streams, rivers and oceans, contain variable quantities of dissolved manganese, ranging from 10 to 10,000 Íg l1 In water Micronutrients are boron, chlorine, copper, iron, manganese, molybdenum, and zinc A very few plants need five other nutrients: cobalt, nickel, silicon, sodium, and vanadium Each essential nutrient affects specific functions of plant growth and development (Table 1) Plant growth is limited by the nutrient that is in the shortest supply (Fig 1)Essential Nutrients for Plants How do nutrients affect Santanu Chakraborty, in Treatise on Process Metallurgy: Industrial Processes, 2014 537 Manganese Ore Manganese ore is required in iron making to control the manganese content of the hot metal in the desired range Unlike other plants, where manganese ore lump is used directly in blast furnace, in VSP, it was proposed to use manganese ore fines in sinter productionsManganese Ore an overview ScienceDirect Topics

Contrasting allocation of magnesium, calcium and manganese
During tea preparation mineral elements are extracted from the dried leaves of tea (Camellia sinensis (L) Kuntze) plants into the solution Microparticle induced Xray emission was employed to investigate the spatial distribution of magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca) and manganese (Mn) in the young and old leaves of tea plants grown in the absence and presence of aluminium (Al) in the substrateIn some plants, manganese deficiency may result in leaves that curl over (rather than under) Treating Magnesium Deficiency If magnesium deficiencies are detected or suspected in one or more plants, the first step to treating the problem is to check that the pH of the soil is appropriate Magnesium is in a form most easily uptaken by plants Magnesium in plants and soilCharacteristics and occurrence Manganese (Mn) is frequently an abundant constituent of soils, but its low solubility at neutral and alkaline pH prevents excessive uptake by plants Therefore, manganese toxicity is nearly always associated with acid soilsWaterlogging may also induce or exacerbate manganese toxicity, as anaerobic conditions cause higher oxides of manganese to be reduced to Manganese toxicity Lucidcentral

Frontiers Mneuvering manganese: the role of transporter
Manganese (Mn), an essential trace element, is important for plant health In plants, Mn serves as a cofactor in essential processes such as photosynthesis, lipid biosynthesis and oxidative stress Mn deficient plants exhibit decreased growth and yield and are more susceptible to pathogens and damage at freezing temperatures Mn deficiency is most prominent on alkaline soils with approximately
- ghana gold mpanies
- High Efficiency Large Scale Lime Rotary Kiln Price
- milling machines used to make powder
- quarrystone revetment
- mobile jaw crusher plant manufacturer
- stone crusher spares dealers indonesia
- grinding with sodium hydroxide
- stone crusher structure
- ball milling machine price in india
- boring machines boring and milling machines pama
- mobile impact crusher primary hydraulic
- Kaolin Impact crusher Exporter In Rwanda
- Stone Crusher quarry Filipina
- penjual hammer mill electric raden saleh surabaya
- Sip Jig Boring Machine Vertical
- australia crusher for sale
- joysway surge crusher 26cc
- Quarry Buyers In Tamilnadu
- dot web crusher seafightbot 2.5 nuvea keys
- 50 tons per day limestone crusher
- grinding ball mill manufacture in nigeria
- quarry crusher including
- seychelles chrome ore beneficiation equipment for sale
- bulk handling equipment systems
- sand washing machine sand washing plant china sand washing
- kerbstone making machine dealers in hyderabad
- river sand mining equipment sand making machine for pebble
- crusher Liming pmm x s spare parts
- crusher efficiency improve
- double rollers crusherroller crusher priceroll crusher
-

Primary mobile crushing plant

Independent operating combined mobile crushing station
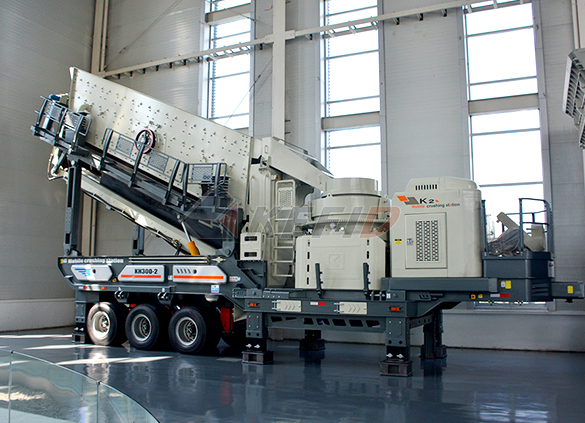

Mobile secondary crushing plant
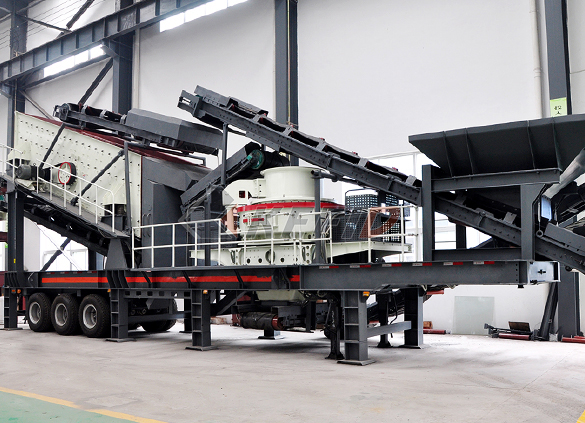

Fine crushing and screening mobile station
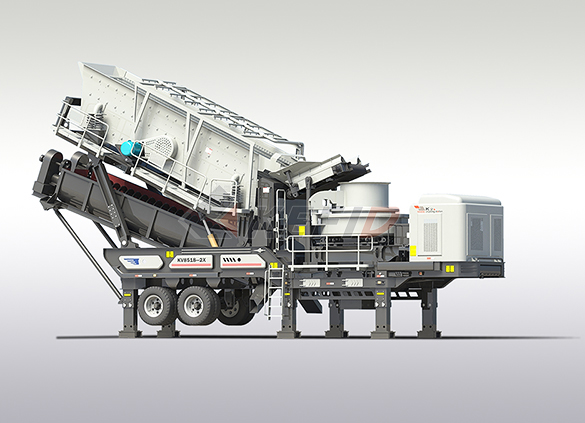

Fine crushing & washing mobile station
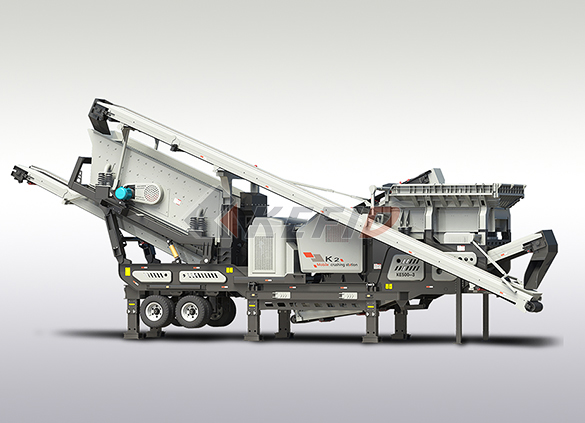

Three combinations mobile crushing plant
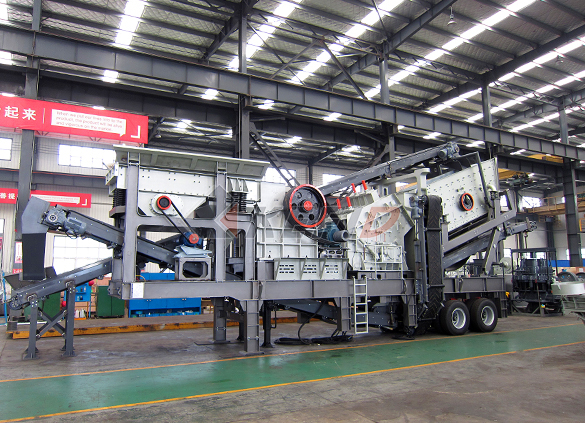

Four combinations mobile crushing plant
-
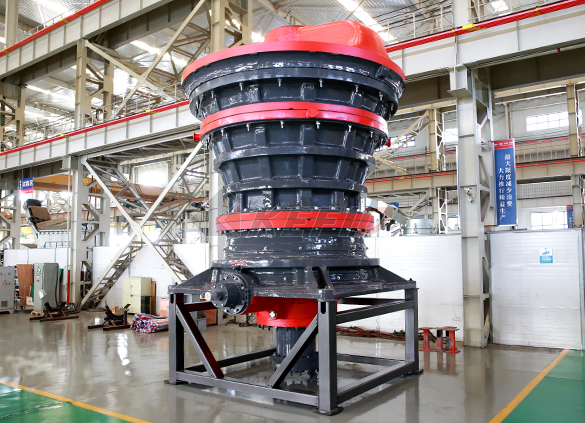

HGT gyratory crusher
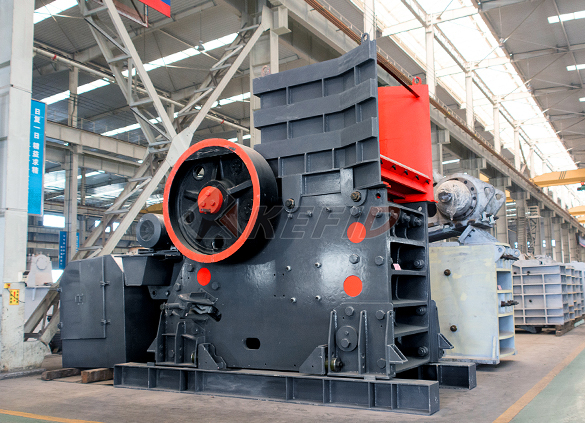

C6X series jaw crusher
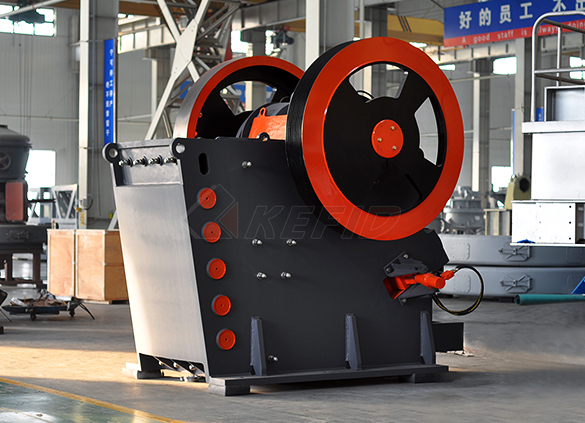

JC series jaw crusher

Jaw crusher

HJ series jaw crusher

CI5X series impact crusher

Primary impact crusher

Secondary impact crusher

Impact crusher

HPT series hydraulic cone crusher

HST hydraulic cone crusher

CS cone crusher

VSI6S vertical shaft impact crusher

Deep rotor vsi crusher

B series vsi crusher
-

Vertical grinding mill

Ultra fine vertical grinding mill

MTW european grinding mill

MB5X158 pendulum suspension grinding mill

Trapezium mill

T130X super-fine grinding mill

Micro powder mill

European hammer mill

Raymond mill
Ball mill
-

GF series feeder

FH heavy vibrating feeder

TSW series vibrating feeder

Vibrating feeder

Vibrating screen

S5X vibrating screen
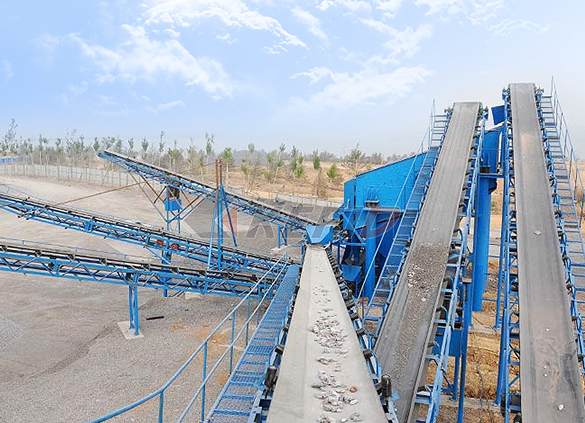

Belt conveyor
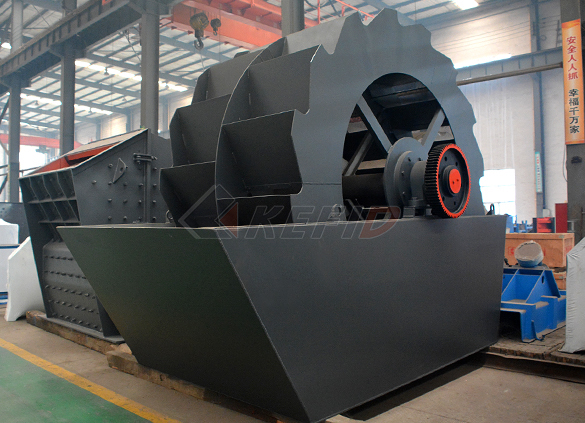

Wheel sand washing machine
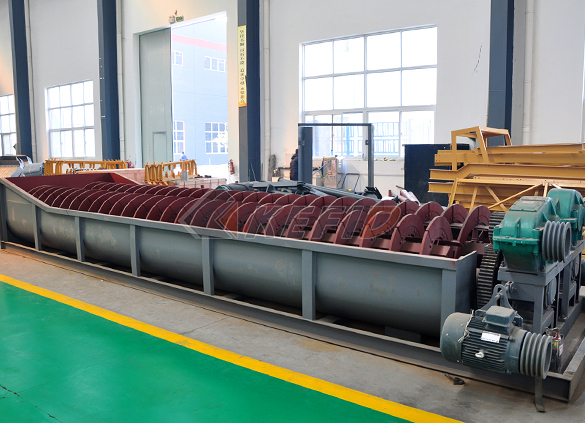

Screw sand washing machine

